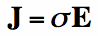Electric Current Density
Electric Current Density
The Electric Current Density is denoted by the vector symbol (J). Electric current is measured in Amps (which is equal to charge per second [C/s]). The current density (which is a volume current density) is measured in Amps per meter squared [A/m^2], because the current flows in a direction, and the area is measured normal/perpendicularly/orthogonally to that. This is shown in Figure 1:
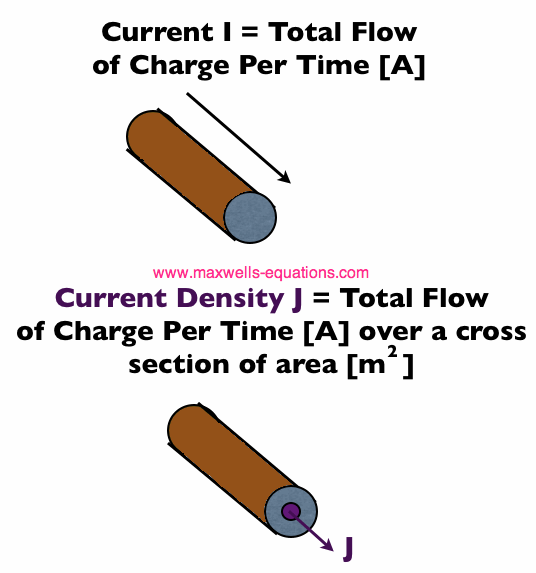 Figure 1. Electric Current I (Top) is The Total Charge Flow Per Second. Current Density J (bottom) is the Current over a Specified Cross Section.
The total electric current (I) can be related to the current density (J) by summing up (or integrating) the current density over the area where charge is flowing:
Note that the current density is often not constant, so a weighted summation (Equation [1]) is needed.
Finally, suppose a medium (material) has an electric conductivity given
by
You may not recognize Equation [3], but it is actually famous - this is Ohm's Law.
You probably know from electric circuits that V=IR, which relates voltage, current and resistance.
In Equation [3], the E-field is analogous to voltage, current density is analogous to current,
and the conductivity Equation [3] states that in a material with a non-zero conductivity, an E-field will produce an electric current.
This page on the electric current density (J) is copyrighted. The copyright belongs to Maxwells-Equations.com, 2012.
|

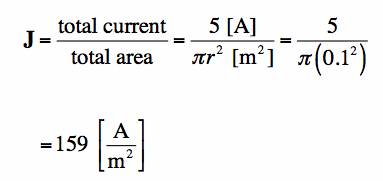
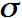 (which is measured in
Siemens/meter, which is the oppose (inverse) of resistance per length).
Then the electric current density can be related to the
(which is measured in
Siemens/meter, which is the oppose (inverse) of resistance per length).
Then the electric current density can be related to the